The shift to remote work, which gained momentum during the pandemic, shows no signs of slowing down. Many teams now juggle their responsibilities from home, enjoying flexibility but also facing new hurdles. Among these, data security stands out as a pressing concern. With employees scattered across various locations, how can companies ensure their sensitive information remains protected? Dive into our blog to uncover the emerging challenges of remote work and discover practical solutions to safeguard your company’s data.
Remote Work Security Challenges
1) Limited Security Oversight
When employees work from home, it’s harder for IT teams to monitor their activities and ensure they follow security protocols. This lack of visibility can lead to remote work security breaches and data loss.
Solution: Implement a robust monitoring system that tracks employee activity, even when they are working remotely. Utilize tools such as VPNs, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems to monitor potential threats effectively. Consider using solutions like SASE to secure remote endpoints. This approach not only encrypts data in transit but also protects the remote devices, mitigating the higher risk of mishandling that can occur outside the office environment.
2) Mishandling Sensitive Data
Employees might not follow best practices when handling sensitive data at home. They could accidentally expose confidential data. It can happen through improper storage or sharing.
Solution: Develop clear policies for handling sensitive data and provide regular training for remote workers. Use encryption and secure file-sharing tools to protect data in transit.
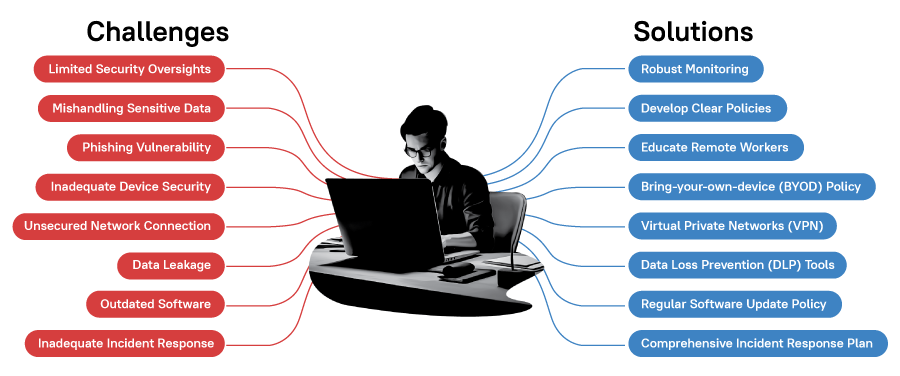
3) Phishing Vulnerability
Phishing attacks have skyrocketed targeting remote workers. Remote workers are 3 times more likely to encounter phishing attacks. Cybercriminals know that home networks are often less secure. They use phishing emails to trick employees into giving away login credentials. This statement is wrong, because phishing emails have nothing to do with home networks.
Solution: Educate remote workers on how to spot phishing attacks and implement anti-phishing software to block suspicious emails. Use two-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security.
4) Inadequate Device Security
Personal devices might not have the same security standards as company devices. It makes them more vulnerable to attacks. Employees might use outdated software or weak passwords. 74% of organizations believe that remote work has increased the likelihood of insider threats.
Solution: Implement a bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policy that requires employees to use company-approved security software and follow best practices for device security.
5) Unsecured Network Connections
Home networks are often less secure than office networks. 47% of employees cited distraction as the reason for falling for a phishing scam while working from home. employees might use weak Wi-Fi passwords or outdated routers. This can expose your data to cyber threats.
Solution: Encourage remote workers to use virtual private networks (VPNs) when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks. This will encrypt their internet traffic and protect company data.
6) Data Leakage
Data leakage can happen through various channels. Employees might accidentally share sensitive information on public platforms. They could also lose devices containing confidential data. Co-working spaces (18%) are the most vulnerable locations for data theft, followed by libraries, coffee shops and cafes.
Solution: Implement data loss prevention (DLP) tools to detect and prevent data leakage. Use encryption and secure file-sharing tools to protect data in transit.
7) Outdated Software
Outdated software is a remote work security risk for those who are working from home. It can have vulnerabilities that hackers exploit. Employees might not update their software regularly when working from home. Almost 39% of organizations have experienced a security incident due to the use of unauthorized software by remote workers.
Solution: Implement a regular software update policy that ensures all remote workers are using the latest versions of company-approved software.
8) Inadequate Incident Response
When a remote work security incident occurs, a quick response is crucial. However, remote work can slow down incident response times. Employees might not know how to report incidents quickly. Approximately, 24% of respondents had to spend money unexpectedly to resolve a security breach or malware attack following the WFH shift.
Solution: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that includes procedures for remote workers. Provide regular training and conduct regular drills to ensure everyone is prepared.
Secure Your Remote Work Future
By strengthening your cybersecurity measures, training employees, and staying vigilant against threats, you can mitigate remote work security risks and ensure a secure remote work environment. Taking proactive steps now will safeguard your organization from potential remote work security breaches in the future.
Is your business struggling with IT and security concerns?
Want to know how to maintain security when employees work remotely? We’ve got your back! Book a call with our experts, and we’ll tailor an affordable solution to keep your business running smoothly.
